Setting Up a Wi-Fi Hotspot on Boot for Your Robot

Index
Why Create a Wi-Fi Hotspot on Boot?
In robotics, self-hosted networks can be critical for:
- Connecting remote controllers or operator devices.
- Transmitting real-time data streams (e.g., images, depth, or control commands).
- Enabling peer-to-peer communication in isolated environments.
Let’s configure a Wi-Fi hotspot to start automatically whenever your robot boots up. 📡🤖✨
Prerequisites
- A Linux-based system (tested on Ubuntu). Our Fetch robot has Ubuntu 18.04 installed.
- NetworkManager installed (commonly pre-installed on Ubuntu).
- A compatible Wi-Fi adapter connected to the robot.
- Root access to the system.
📋 Ensure these are set up before proceeding!
Step 1: Create the Hotspot Script
Let’s have a directory related to this setting:
# try setting absolute path
export WIFI_ADAP_ROOT_DIR=/home/fetch/wifi-adapter-settings
mkdir -p $WIFI_ADAP_ROOT_DIR
cd $WIFI_ADAP_ROOT_DIR
We’ll use a Bash script to configure and start the hotspot. Create the file start_hotspot.sh:
#!/bin/bash
# Disable the firewall
ufw disable
echo "Firewall stopped and disabled on system startup"
# Wait for 2 seconds
sleep 2
# Read credentials and create hotspot
CREDS_FILE=$WIFI_ADAP_ROOT_DIR/hotspot_creds.cfg
source $CREDS_FILE
# Create the hotspot
nmcli device wifi hotspot ifname alpha_wifi_adap ssid "$SSID" password "$PASSWORD" band a channel 149
Explanation of the Script:
- Disable the firewall: Ensures no network traffic is blocked (adjust this for secure setups).
- Wait for 2 seconds: Adds a buffer to ensure system services are up.
- Source credentials: Reads the hotspot name (SSID) and password from hotspot_creds.cfg.
- Set up the hotspot: Uses nmcli to configure and start the hotspot.
Save this script to $WIFI_ADAP_ROOT_DIR/start_hotspot.sh and make it executable:
chmod +x $WIFI_ADAP_ROOT_DIR/start_hotspot.sh
Step 2: Create a Credentials File
Store your hotspot credentials in a secure configuration file:
nano $WIFI_ADAP_ROOT_DIR/hotspot_creds.cfg
Add the following content:
SSID="your_hotspot_name"
PASSWORD="your_secure_password"
Make sure the credentials file is readable only by the owner:
chmod 600 $WIFI_ADAP_ROOT_DIR/hotspot_creds.cfg
🛡️ This keeps your credentials secure!
Step 3: Create a Systemd Service
To ensure the hotspot script runs on every boot, create a systemd service file:
sudo nano /etc/systemd/system/start_hotspot.service
Add the following content:
[Unit]
Description=Start Hotspot Script on Boot
After=network.target
[Service]
Type=oneshot
ExecStart=/bin/bash /home/fetch/wifi-adapter-settings/start_hotspot.sh
RemainAfterExit=yes
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
Explanation of the Service File:
- After=network.target: Ensures the service starts after network services are ready.
- ExecStart: Runs the hotspot script. NOTE: Keep the absolute path of the script.
- RemainAfterExit: Keeps the service active after execution.
Enable the service:
sudo systemctl enable start_hotspot.service
Test the service by starting it manually:
sudo systemctl start start_hotspot.service
sudo systemctl status start_hotspot.service
If successful, the hotspot should start without errors. 🚀✨
Step 4: Verify Hotspot on Boot
To confirm the hotspot starts correctly after reboot:
- Reboot your system:
sudo reboot - Once the system boots up, check the hotspot status:
sudo systemctl status start_hotspot.service - You can also use the nmcli command to verify:
nmcli dev wifi
✅ This ensures everything is working smoothly! 🌟
Step 5: Optional – Add Status Check to ~/.bashrc
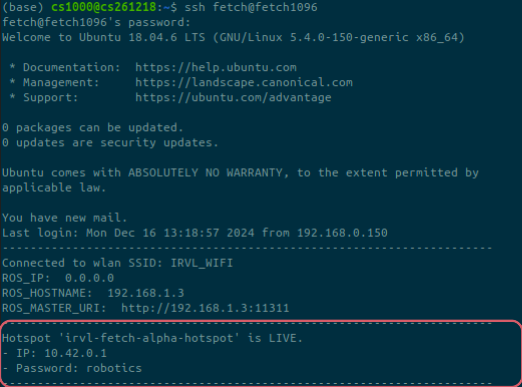
For convenience, add a status check to your ~/.bashrc file. This will display the hotspot’s status whenever you open a terminal:
# Check Hotspot Status, use absolute path
CREDS_FILE=/home/fetch/wifi-adapter-settings/hotspot_creds.cfg
if [ -f $CREDS_FILE ]; then
source $CREDS_FILE
if nmcli dev wifi | grep -q "$SSID"; then
ip_address=$(ip addr show alpha_wifi_adap | grep 'inet ' | awk '{print $2}' | cut -d/ -f1)
echo "Hotspot '$SSID' is LIVE."
echo -e "- IP: $ip_address
- Password: $PASSWORD"
else
echo "Hotspot '$SSID' is NOT ACTIVE."
fi
else
echo "Hotspot credentials file not found."
fi
Right: A demo showcasing the HoloLens connecting to the created hotspot.
Troubleshooting
- Error: Not authorized to control network:
- Ensure the script is executed with root privileges.
- Error: either ‘dev’ is duplicate or ‘iwlist’ is garbage:
- Verify the hotspot interface name (alpha_wifi_adap).
- Double-check the hotspot script syntax.
- Hotspot not starting on boot:
- Check the service logs:
sudo journalctl -u start_hotspot.service
- Check the service logs:
🛠️ Be ready to debug as needed! 🧩
Feel free to reach out in case you have a query. You are always welcome. You can find me on X at @jis_padalunkal.